California sees thousands of crashes every year, many caused by the same recurring factors: distracted driving, speeding, DUI, reckless behavior, fatigue, unsafe roads, defective vehicles, inexperienced drivers, and hazardous weather. Each of these dangers can be prevented through safer driving habits, increased awareness, and accountability from drivers, manufacturers, and government agencies.
We have listed down not just the leading causes of California crashes, but also the preventative measures drivers overlook, the legal consequences reckless motorists face, and how victims can use the law to recover after an accident.
Top 10 Causes and Prevention of Car Accidents in California
1. Distracted Driving: The Leading Cause of Urban Collisions
The Insurance Institute for Highway Safety (IIHS) reported that distracted driving was involved in 10,198 crashes in 2024, accounting for 6.2% of all collisions.
With drivers navigating crowded streets, complex intersections, and freeway merges, even a moment of inattention can have devastating consequences.
In legal terms, distracted driving isn’t just unsafe. It’s a clear breach of a driver’s duty of care, opening the door to liability in personal injury claims.
Texting, Scrolling, and Hands-Off Driving Behaviors
In 2024 alone, out of 10,198 motor crashes, 12% involved drivers actively using their phones- whether texting or casually scrolling. Beyond mobile use, other hands-off activities such as adjusting a GPS, eating, or drinking, remain major contributors to collisions. These distractions, especially in heavy traffic, often escalate minor lapses into serious crashes.

Prevention Tip
Keep your phone completely out of reach while driving, in the glove compartment, back seat, or switched off. Do not text, scroll, eat, or adjust devices until the vehicle has come to a full stop in a safe location. If navigation is necessary, set your GPS before starting the trip and use only voice-activated or hands-free controls that are mounted and hands-free. Any handheld use behind the wheel poses a direct risk to your life and that of others.
2. Speeding on Congested Freeways
Speeding contributes to nearly one in three fatal crashes - and on California’s crowded freeways, the danger is magnified. It’s not only about breaking the posted limit; speeding also means driving too fast for road, traffic, or weather conditions. In heavy congestion, even a small mistake at high speed can set off a chain-reaction crash, putting dozens of lives at risk within seconds.
Prevention Tip
Do not exceed the posted limit, and in congested areas, drive well below it. Treat every freeway jam as a high-risk zone: maintain a following distance of at least three seconds, avoid sudden lane changes, and reduce speed the moment traffic thickens or weather conditions change. If you feel pressured by aggressive drivers, hold your lane at a safe, steady speed instead of matching their pace. On congested freeways, the only safe rule is this: if you aren’t fully in control, you’re driving too fast.
I-405, I-10, and Known High-Speed Zones
Los Angeles freeways such as the I-405 (San Diego Freeway) consistently rank among the most congested in the nation. In these conditions, speeding doesn’t just heighten the risk of crashes - it significantly increases driver liability when accidents occur.
The I-10, especially along downtown and the Santa Monica Freeway, is another hotspot where dense, multi-lane traffic mixes with complex interchanges and last-second lane changes. Combined with high speeds, these factors create a perfect storm for catastrophic freeway collisions.
Crash Rates vs. Posted Speed Limits
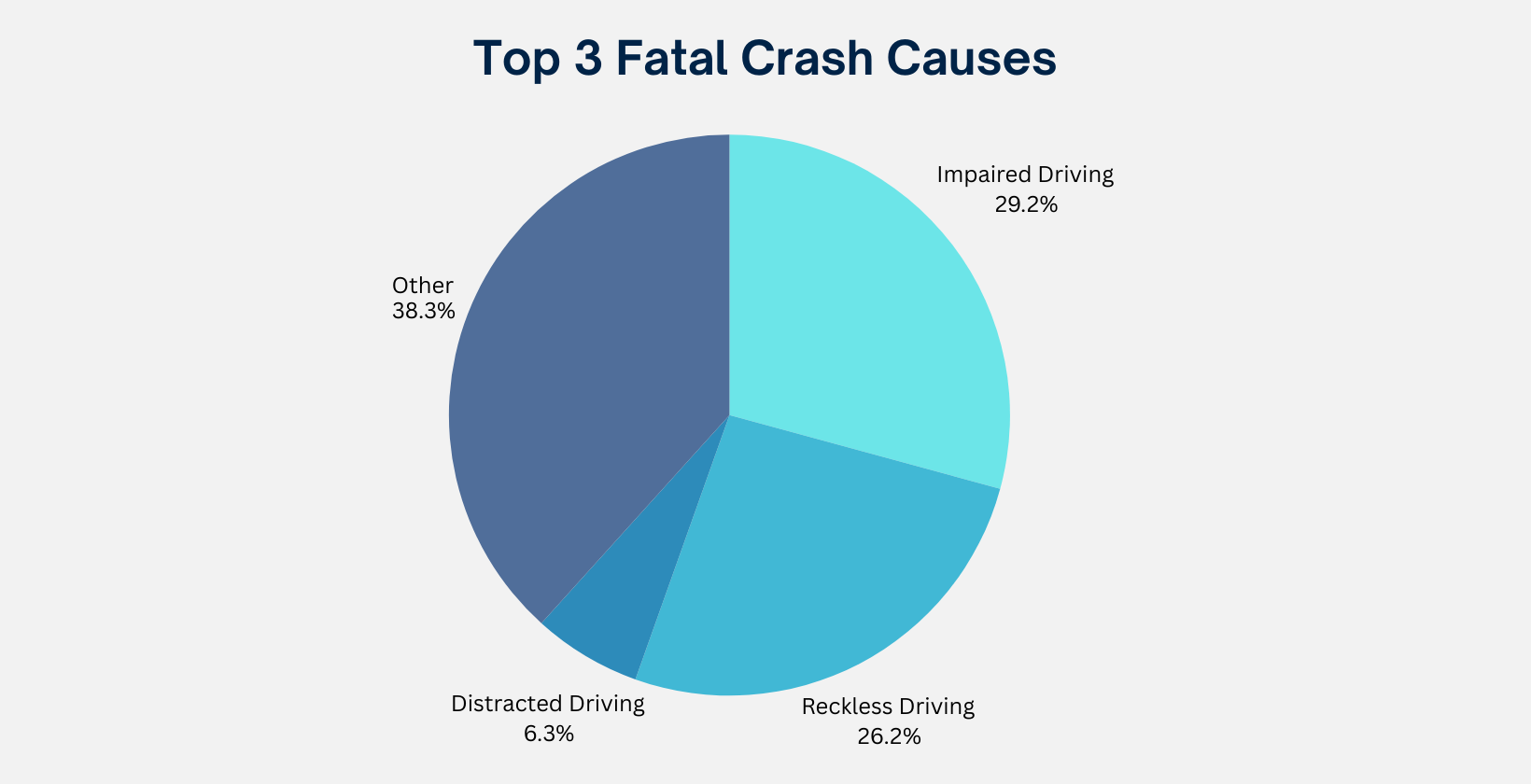
Speeding contributed to 29% of U.S. road deaths in 2024. In California, lowering average speed by just 1 mph can reduce crashes by up to 7%. On freeways like I-405 and I-10, even slight speeding in curves, merges, or congestion can turn routine traffic into deadly collisions.
3. Driving Under the Influence (DUI)
Alcohol and Cannabis-Related Impairments

Prevention Tip
Never drive after drinking or using cannabis, even in small amounts. If impaired, use a rideshare service, taxi, or designate a sober driver. One choice can prevent a fatal crash and a DUI charge.
DUI Statistics and Arrest Patterns in CA
DUI causes nearly 30,000 crashes and 29% of road deaths in California. Most arrests involve alcohol, though cannabis-related DUIs continue to rise. Peak arrest times are typically between 11:00 p.m. and 3:00 a.m., with weekends seeing the highest concentrations of impaired-driving stops.
4. Reckless Driving & Aggressive Behavior
Lane Weaving, Tailgating, and Illegal Overtakes
Aggressive drivers often stack risky moves, weaving through lanes, tailgating, or overtaking illegally in seconds. These aren’t minor infractions; they’re reckless violations of the duty of care. In 2024, such behaviors contributed to 2,251 traffic deaths across California.
Prevention Tip
Never tailgate, weave, or overtake illegally. Leave a safe distance, obey signals, and slow down, reckless moves turn deadly in seconds.
Legal Consequences for Aggressive Driving
Reckless driving carries serious penalties under California law. Offenders may face fines of up to $1,000, imprisonment for up to 90 days, or both. A conviction can also result in license suspension. If the reckless act causes injury, the penalties escalate sharply, with harsher fines, longer jail terms, and lasting consequences on driving and criminal records.
5. Running Red Lights & Stop Signs
Prevention Tip
Always come to a full stop and obey every signal. Never rush through yellows or roll through stop signs - one reckless choice can cost lives.
California Ranked Worst State for Red-Light Running Car Accidents
California leads the nation in deadly red-light violations. In 2019, the state recorded nearly 130 fatal crashes caused by drivers running red lights, accounting for a large share of the 840 deaths nationwide that year.
6. Driver Fatigue and Drowsy Driving
Fatigue leaves no chemical trace, yet its impact rivals that of alcohol or drugs; it causes delayed reactions, poor judgment, and dangerous “microsleeps” where drivers can veer off course without noticing. In California, choosing to drive while dangerously drowsy can still establish negligence, even if it does not lead to a crash.

Prevention Tip
Never drive when drowsy. If you feel your eyes heavy or reaction time slowing, pull over and rest. Schedule breaks, share long drives, and treat sleep as non-negotiable before getting behind the wheel.
Work Shifts, Impaired Judgment, and Slower Reaction Time
Night-shift workers, rideshare drivers, and long-haul truckers face high fatigue risks. NIOSH reports that 17 hours without sleep impairs drivers as much as a 0.05% BAC, while 24 hours awake is equivalent to a 0.10% BAC, which is well over the legal limit.
7. Poor Road Conditions & Construction Zones
Unsafe roads often play a direct role in crashes. Uneven pavement, faded markings, and poorly managed construction zones can quickly turn an ordinary drive into a dangerous or even deadly accident, even for the most cautious drivers.
Potholes, Incomplete Lanes & Confusing Signage
Deep potholes can cause drivers to lose control or swerve dangerously, potentially leading to accidents. Narrowed or unfinished lanes often force sudden merges, leading to sideswipes and rear-end crashes. Missing or faded signage further delays reactions and increases confusion. When these hazards exist without proper warnings, collision risks rise sharply, and liability may extend to road authorities or contractors, not just the drivers.
Prevention Tip
Slow down in construction zones and on roads with damage. Keep extra distance, avoid sudden swerves, and treat missing signs or lane shifts as high-risk hazards.
Caltrans Maintenance Gaps and Liability Questions
8. Vehicle Defects & Mechanical Failures
Not all crashes are caused by driver error; many in California stem from mechanical failures or defective auto parts that trigger loss of control and serious accidents. In such cases, liability may extend beyond the driver to the vehicle manufacturer, parts supplier, or even the repair shop. These claims often fall under product liability law, which holds automakers accountable for defective designs, faulty manufacturing, or inadequate safety warnings.
Brake Failure, Tire Blowouts, and Steering Malfunctions
Defective brakes, tire blowouts, and steering failures are among the most dangerous mechanical issues, often leading to loss of control, rollovers, or multi-vehicle pileups. Determining liability can be complex, with responsibility potentially falling on the manufacturer, repair shop, or even the vehicle owner for inadequate maintenance.

Prevention Tip
Never ignore warning lights or unusual noises. Schedule regular inspections, replace worn parts immediately, and follow recall notices without delay; neglecting maintenance can be deadly.
Manufacturer Recalls & Legal Recourse Options
Widespread defects often lead to manufacturer recalls, requiring free repairs or replacements. But recalls don’t erase liability for crashes that occurred beforehand, and delays in issuing a recall can create additional responsibility for the automaker. Victims of defect-related accidents may pursue multiple legal avenues, including product liability, negligence, and breach of warranty claims.
9. Inexperienced & Unlicensed Drivers
California’s busy roadways pose a challenge even to the most experienced motorists, and for inexperienced or unlicensed drivers, the dangers are multiplied. Legally, inexperience is no defense for unsafe driving. Whether a driver is new behind the wheel or operating without a valid license, they are still bound by the same duty of care under California law and can be held fully liable for the harm they cause.
Teenage Drivers and Out-of-State Visitors
Teen drivers carry a heightened risk of crashes, often due to inexperience, distraction, and overconfidence. CHP data shows drivers aged 16-19 face some of the highest collision rates, particularly in their first year of licensure.
Out-of-state visitors face different hazards, unfamiliarity with high-speed merges, complex interchanges, and crowded intersections. Tourists often depend heavily on GPS, which can lead to sudden lane changes, missed exits, and distracted driving.
Driver Training Gaps and Permit Violation Cases
Drivers who skip proper training or rely on minimal practice just to pass licensing tests often create serious crash risks. Some operate illegally, driving without a license or on a learner’s permit. These violations are more than criminal offenses; they can also strengthen civil claims. In personal injury cases, showing that the at-fault driver lacked proper licensing or training highlights that they were never legally qualified to be on the road, reinforcing negligence.
Prevention Tip
Never drive without proper training or a valid license. Parents must closely supervise teens, and visitors should study local traffic laws, ignorance or inexperience is no excuse when lives are at stake.
10. Weather Conditions & Environmental Hazards
An estimated 70-75% of weather-related crashes occur on wet roads. Many drivers underestimate the dangers of rain, fog, or glare, yet these conditions demand greater caution. Under California law, motorists are required to adjust speed and driving behavior to match road and weather conditions, meaning poor weather is rarely a valid defense against negligence.
Rain-Induced Skidding and Poor Visibility
In Los Angeles, the first rainfall after dry spells leaves roads slick and prone to hydroplaning. Fog, heavy downpours, and glare further cut visibility, making collisions far more likely when drivers fail to slow down or maintain a safe distance. Under California law, ignoring these hazards and driving at unsafe speeds can strongly support a negligence claim.

Preventive Tip
Slow down, increase following distance, and use headlights in rain or fog. Never assume normal stopping power in bad weather; caution is the law.
The Role of Infrastructure in Weather-Related Crashes
Driver behavior is critical, but infrastructure failures also fuel weather-related accidents. Clogged or poorly maintained storm drains can create deep pools that conceal potholes and trigger hydroplaning. Faded or missing lane markings make navigation even more hazardous in heavy rain or fog, increasing the likelihood of collisions.
California Car Accident Statistics: What’s Really Causing the Rise
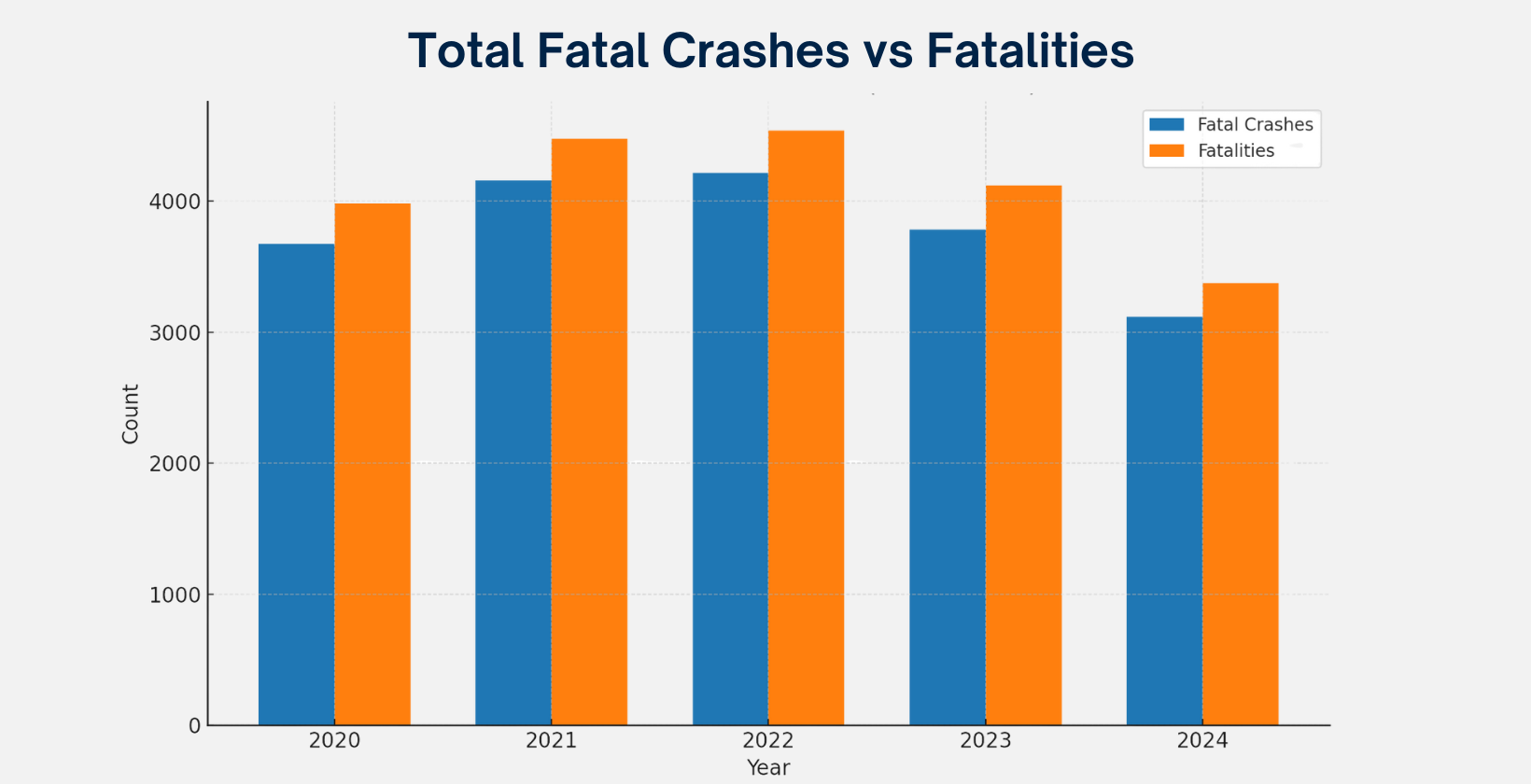
Car accidents remain a pressing concern across California. While fatality numbers fluctuate year to year, the state still records thousands of deaths and tens of thousands of injuries annually. Data from CHP and NHTSA reveal a troubling pattern; urban crash rates continue to climb, even as overall statewide fatalities show signs of decline.
For a closer look at the most recent numbers, yearly comparisons, and contributing factors, explore our full breakdown of car accident statistics in California (2025).
California Statewide Traffic Fatalities Data Breakdown by Cause (2020–2024)
Total Fatal Crashes vs Fatalities
Top 3 Fatal Crash Causes
Los Angeles: The Riskiest County For Traffic-Related Incidents In CA
- Average of 60,000 fatalities and injuries annually
- 11,120 crashes recorded in 2024 alone
- More than 25% of all pedestrian deaths
High-Risk Intersections and Freeway Exits
- Devonshire St & Reseda Blvd
- Imperial Hwy & Vista Del Mar
- Balboa Blvd & Nordhoff St
Common Types of Car Accidents in California
Rear-End Collisions at Intersections
T-Bone Crashes in High-Speed Zones
Sideswipe Accidents from Unsafe Lane Changes
Single Vehicle Accidents from Loss of Control
Hit-and-Run Crashes in Urban Areas
Multi-Vehicle Pileups on Freeways
What You Need to Know Legally After a Car Accident in California
Critical First Steps After the Crash
- Call 911 and check for injuries
- Get medical care immediately
- Exchange insurance and driver info
- Never admit fault
- Document the scene with photos and witness details
- Contact a Los Angeles car accident lawyer promptly
Note: Failing to report a crash to the DMV within 10 days (if damages exceed $1,000 or injuries/fatalities occur) can result in license suspension.
When to Contact a Car Accident Attorney
Contact a lawyer right away, ideally the same day. Legal help is critical if:
- Injuries or hospitalization occurred
- The insurer offers a quick settlement
- Fault is disputed or multiple vehicles are involved
- Future medical costs are uncertain
What Evidence Strengthens a Personal Injury Claim
- Police reports and crash reconstructions
- Medical records and treatment notes
- Witness statements
- Photos/videos of the scene, vehicles, and injuries
- Insurance communications
Statute of Limitations and Key Deadlines in California
- 2 years from the accident to file a personal injury claim (Cal. Civ. Proc. Code §335.1)
- 6 months to file against a government entity (Gov’t Code §911.2)
When Prevention Isn’t Enough: Get Legal Help After a Car Accident
Even the safest drivers can’t control every situation. Crashes still happen, often because of another driver’s negligence, defective vehicles, or hazardous road conditions. If you or a loved one were injured despite taking every precaution, you shouldn’t have to shoulder the burden alone.
At Blair & Ramirez LLP, our car accident lawyers will investigate your case, hold the at-fault parties accountable, and fight for the maximum compensation you deserve, while you focus on recovery.

Tell Us What Happened - We’re Ready to Help

