Head injuries are among the most serious and unpredictable injuries you can sustain. In the time it takes to be injured, your life can be irrevocably altered, and the path toward your most complete recovery is certain to be challenging. If you’ve suffered a head injury as a result of someone else’s negligence, you should not delay discussing your claim with an experienced head injury lawyer in Los Angeles – your future could depend upon it.
What Is a Head Injury?
Created by Blair & Ramirez LLP. Contact Us
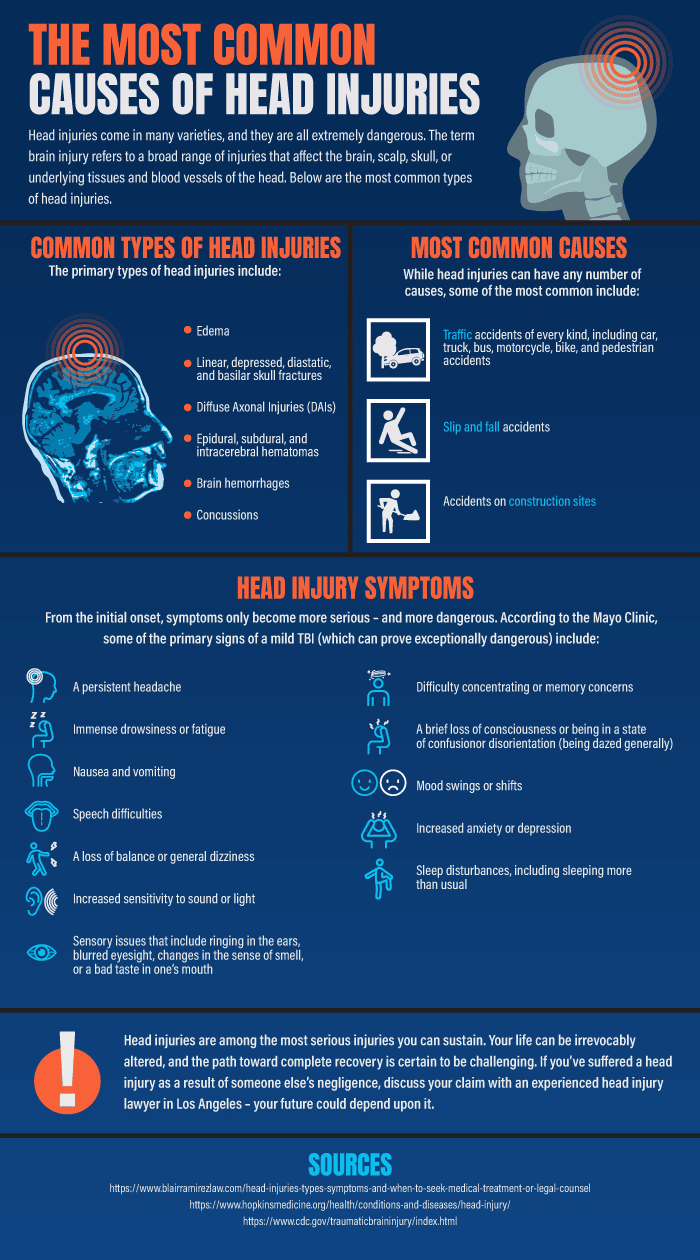
The Primary Types of Head Injuries
Hematomas
Intracranial hematomas (ICH) refer to blood clots in or around the brain, and there are several basic categories, which are classified according to their location. These injuries can range from mild to life-threatening:
- Epidural hematomas – An epidural hematoma is a blood clot that forms underneath the skull but on top of the brain’s tough covering. This type of hematoma is typically associated with skull fractures.
- Subdural hematomas – A subdural hematoma is a blood clot that forms underneath the skull and the brain’s tough covering but outside the brain itself. It can form as a result of a tear that travels from the brain to its covering and is sometimes associated with skull fractures.
- Contusions (or intracerebral hematomas) – A contusion or intracerebral hematoma refer to a bruise on the brain itself. These injuries cause the brain to bleed and swell in the area in which the brain was struck.
Hemorrhages
Concussions
A concussion is a type of TBI that can lead to an instantaneous loss of alertness or awareness and can last from a few seconds or minutes to several hours. Concussions related to contact sports have received considerable press in recent years due to the serious cumulative damage associated with repeated concussions.
Edema
Skull Fractures
A skull fracture refers to an actual break in the skull bone. There are several basic types (Johns Hopkins Medicine), including:
- Linear skull fractures – Linear skull fractures are the most common type of skull fracture, and they refer to a break in the skull bone that does not move the skull bone. Linear skull fractures generally require little treatment other than an observation period in the hospital.
- Depressed skull fractures – Depressed skull fractures refer to injuries in which the trauma involved actually causes a sunken depression in the part of the skull that experiences it. Surgical intervention may be required to address the physical deformity caused.
- Diastatic skull fractures – Diastatic skull fractures refer to fractures that happen along the skull’s suture lines (those areas between the bones that make up our heads and that fuse when we are very young). These fractures are seen mainly in newborn babies and other infants.
- Basilar skull fractures – Basilar skull fractures are the most serious skull fractures of all, and they refer to a break in the bone that forms the base of the skull. Common signs of these fractures include telltale bruises around the eyes that are accompanied by a bruise behind the ear. Victims can also exhibit clear drainage from the ears or nose (caused by a tear in the brain’s covering).
Diffuse Axonal Injuries (DAIs)
DAIs refer to the kinds of head injuries that are commonly associated with car accidents, slip and fall accidents, and other occurrences in which the head is shaken back and forth on the neck.
Most Common Causes
While head injuries can have any number of causes, some of the most common include:
- Traffic accidents of every kind, including car, truck, bus, motorcycle, bike, and pedestrian accidents
- Slip and fall accidents
- Accidents on construction sites
When You Should See a Doctor
The Mayo Clinic reminds everyone that if you’ve taken a blow to the head or body that concerns you in any way – or that causes you to exhibit behavioral changes – you should seek medical attention. If you exhibit any signs that are indicative of a TBI or another kind of brain injury, you should seek emergency medical care. If you are on the fence about whether medical attention is really necessary, it’s important to recognize that erring on the side of caution is always in the best interest of your health. Remember that early diagnosis is very closely associated with improved prognosis and obtaining the medical care you need sooner rather than later.
Bob Saget
Head Injury Symptoms
According to the Mayo Clinic, some of the primary signs of a mild TBI (which can prove exceptionally dangerous) include:
- A persistent headache
- Immense drowsiness or fatigue
- Nausea and vomiting
- Speech difficulties
- A loss of balance or general dizziness
- Increased sensitivity to sound or light
- Sensory issues that include ringing in the ears, blurred eyesight, changes in the sense of smell, or a bad taste in one’s mouth
- Difficulty concentrating or memory concerns
- A brief loss of consciousness or being in a state of confusion or disorientation (being dazed generally)
- Mood swings or shifts
- Increased anxiety or depression
- Sleep disturbances, including sleeping more than usual
From here, the symptoms only become more serious – and more dangerous. It’s important to note here that, although TBIs are classified as mild, moderate, and severe, these distinctions refer only to how the injuries affect your brain’s functioning. As such, even a mild TBI can prove exceptionally dangerous and should be taken very seriously.
Types of Treatments for Head Injuries
The Mayo Clinic shares the treatment protocols for head injuries in different situations.
Medication
Medications are often employed to help limit secondary damage to the brain in the immediate aftermath of a brain injury, including:
- Anti-seizure medications – During the first week after a moderate to severe TBI, victims are at increased risk of having seizures, and anti-seizure medications are often prescribed during this period.
- Diuretics – Because diuretics help reduce the volume of fluids in people’s tissues, IV diuretics are sometimes prescribed for those with brain injuries to help reduce pressure within the brain.
- Coma-inducing drugs – Because a comatose brain requires less oxygen to function properly, temporary comas are sometimes induced for people who’ve suffered brain injuries (especially if the injury is depriving the victim’s brain of much-needed oxygen and nutrients).
Surgery
Sometimes, surgery is necessary to reduce the risk of additional brain damage. Common examples include surgeries that are intended to do all the following:
- The removal of hematomas
- The repair of skull fractures
- The stoppage of bleeding in the brain
- The relief of pressure in the brain
Rehabilitation
People who have suffered TBIs often require rehabilitation to support and improve their ability to engage in the activities of daily living. Common forms of rehabilitation include:
- Physical therapy
- Occupational therapy
- Speech and language therapy
- Psychiatric rehabilitation
- Neuropsychological rehabilitation
- Recreational therapy
- Vocational therapy
In addition to the therapists themselves, the kinds of professionals involved often include social workers, case managers, rehab nurses, TBI nurse specialists, counselors, and more.
Long Term Effects
When to Seek Legal Counsel
If you’ve suffered a brain injury, you may be at an utter loss for how best to proceed, and the thought of hiring a brain injury lawyer may be daunting. The fact is that if you have suffered a brain injury as a result of someone else’s negligence, obtaining just compensation that covers your physical, financial, and emotional losses can mean the difference between your ability to recover to the extent possible and failure to do so. If you find yourself in this challenging situation, it’s always in your best interest to seek the professional legal counsel of an experienced brain injury lawyer in Los Angeles.
Results of Head Injury Cases in Los Angeles
At Blair & Ramirez LLP in Los Angeles, we have an impressive track record of helping clients like you who’ve suffered brain injuries as a result of someone else’s negligence fully recover on their complete range of losses – in pursuit of their most complete recoveries.